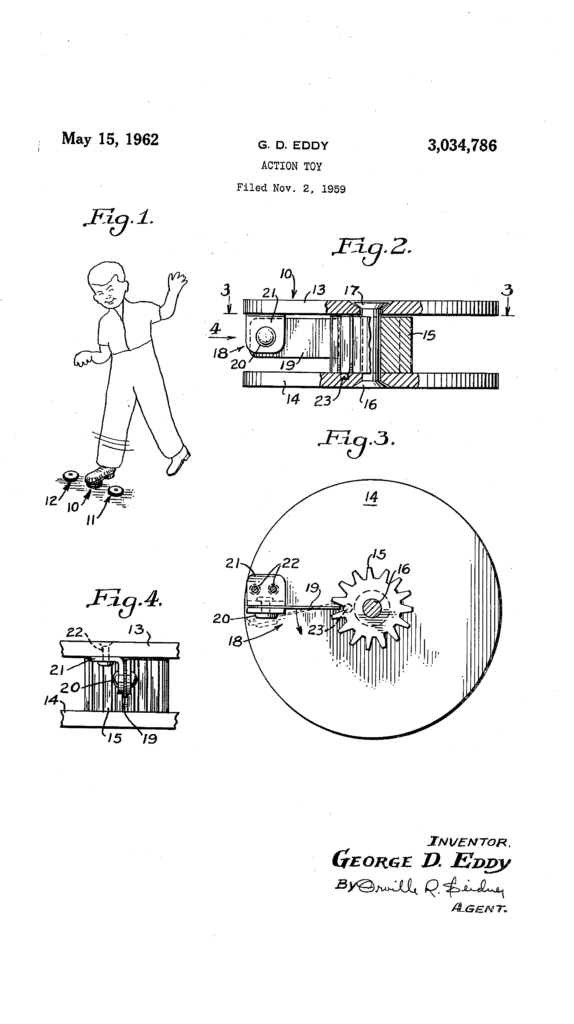
In Malvern Panalytical Inc., v. TA Instruments-Waters LLC, [2022-1439] (November 1, 2023), because the district court erred in construing “pipette guiding mechanism,” the Federal Circuit vacated the stipulated judgment of non-infringement of U.S. Patent Nos. 8,827,549 (“the ’549 patent”) and 8,449,175 and remanded for further proceedings. These patents both disclose microcalorimeters, which are machines that measure the amount of energy absorbed or released during a chemical reaction between two compounds.
Malvern and Waters disputed whether the term “pipette guiding mechanism” encompasses only manual guiding mechanisms (Waters’s position) or covers both manual and automatic guiding mechanisms (Malvern’s position). The Federal Circuit agreed with Malvern that “pipette guiding mechanism” means a mechanism that guides the pipette assembly manually or automatically.
Starting with the claim language, the Federal Circuit concluded that “pipette guiding mechanism” has a plain and ordinary meaning—a mechanism that guides the pipette assembly. It is appropriate to construe this term by looking to the words “pipette,” “guiding,” and “mechanism” individually. Looking at the individual words in the claim, the immediately apparent meaning is that a “pipette guiding mechanism” is a mechanism that guides the pipette. The claim language contains no restrictions that would suggest that the “pipette guiding mechanism” is only manual. Instead, the broad claim language supports the conclusion that the “pipette guiding mechanism” encompasses both manual and automatic embodiments.
The specification confirms the broader understanding of the “pipette guiding mechanism.” It discloses two embodiments of the guiding mechanism. The first embodiment is a guide arm that can move only by way of a guide rod where permitted by guide grooves. The second is a guide arm that can only move where permitted by a coaxial guide sleeve. The specification contains no language describing the invention as limited to a manual guiding mechanism, stating that “the present invention ‘is,’ ‘includes,’ or ‘refers to’” a manual guiding mechanism, or “expressing the advantages, importance, or essentiality” of a manual guiding mechanism.
The district court took a different view, concluding that “pipette guiding mechanism” is a coined term with no commonly understood meaning in the art. On this basis, the district court concluded that “pipette guiding mechanism” “cannot be construed broader than the disclosure in the specification.” The Federal Circuit said that it has sparingly applied this principle of construction in other cases. The district court’s analysis predominantly addressed whether “pipette guiding mechanism” has a plain and ordinary meaning broadly in the art. The Federal Circuit said that this analysis, however, did not answer the question of what plain and ordinary meaning a term has in the context of a patent, which is the focus of the Federal Circuit’s analysis. The Federal Circuit said that it discerns plain and ordinary meaning by examining the claims themselves, the specification, and the prosecution history.
The district court relied heavily on the co-owned, but unrelated ’782 patent prosecution history to limit the guiding mechanism to manual embodiments. The Federal Circuit concluded that merely listing the ’782 patent office actions in the IDS of the patent supplemental examination was insufficient to inform the meaning of “pipette guiding mechanism” in the unrelated ’175 and ’549 patents. On this basis, the Federal Circuit concluded that the district court erred when it used the ’782 patent prosecution history statements to limit “pipette guiding mechanism” to manual guiding mechanisms. The Federal Circuit said:
“In the absence of an incorporation into the intrinsic evidence, this court’s precedent takes a narrow view on when a related patent or its prosecution history is available to construe the claims of a patent at issue and draws a distinct line between patents that have a familial relationship and those that do not.”
The amount of characterization of that reference in the IDS impacts how informative we consider that reference when evaluating a patent. For example, listing of references in an IDS does no more than admit “that references in the disclosure may be material to prosecution of the pending claims,” but it does not admit materiality. Likewise, a patentee has not necessarily admitted that a listed reference’s characterization or use of a claim term bears on the proper construction of that term in the patent.
The Federal Circuit noted that although the ’782 patent applicant argued that the ’968 application discloses only a manual guiding mechanism, the examiner clearly stated its rejection of this argument several times. In these circumstances, where an applicant abandons its unsuccessful argument, the Federal Circuit concluded that the prosecution history lacks the clarity necessary to establish prosecution disclaimer.